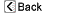Inflammatory bowel disease
| Normal anatomy |
|
The gastrointestinal tract starts at the mouth, which leads to the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, and finally, the rectum and anus. The GI tract is basically a long, hollow, muscular tube through which food passes and nutrients are absorbed.
|
|
| Indications |
|
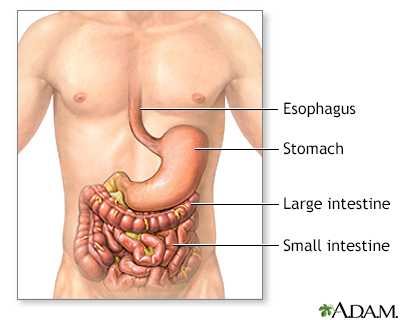
Inflammatory bowel disease is a condition in which the innner lining of the GI tract becomes inflamed, leading to ulcers and bleeding. The colon is most often the site of this inflammation. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease have symptoms that include diarrhea, abdominal pain, infections, and bleeding. Inflammatory bowel disease falls under two main headings: Crohn's disease, which involves the entire GI tract, and ulcerative colitis, which involves only the colon. The cause of inflammatory bowel disease is unknown.
|
|
| Incision |
|
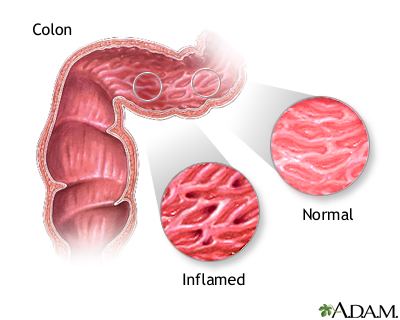
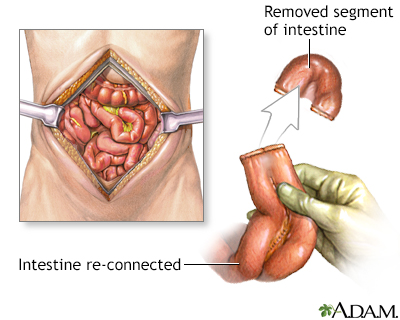
The primary treatment for inflammatory bowel disease involves medications, such as steroids, which can decrease inflammation and resolve symptoms. Occasionally, if segments of bowel are very inflamed and are not responding to medication, surgery to remove these segments may be necessary. While the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia), an incision is made in the midline of the abdomen.
|
|
| Procedure |
|
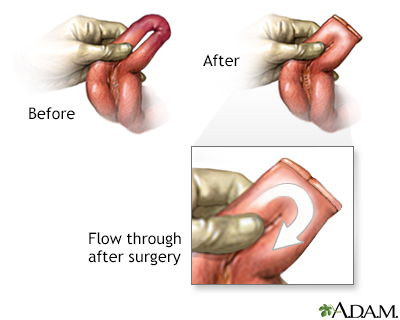
The inflamed segment of the colon or small intestine is removed and the healthy ends are sewn back together.
|
|
| Aftercare |
|
The removal of one section does not preclude recurrence of symptoms in other areas of the intestine. The course of inflammatory bowel disease is often variable: Some patients experience only mild symptoms, while others have more debilitating symptoms.
|
|
|
Review Date:
1/24/2025
Reviewed By:
Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. � 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
� 1997-

All rights reserved.