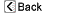Diaphragmatic hernia repair
| Normal anatomy |
|
The chest cavity includes the heart and lungs. The abdominal cavity includes the liver, the stomach, and the small and large intestines. The two regions are separated by the diaphragm, the large dome-shaped muscle.
|
|
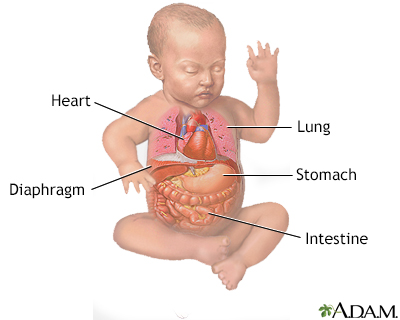
| Indication |
|
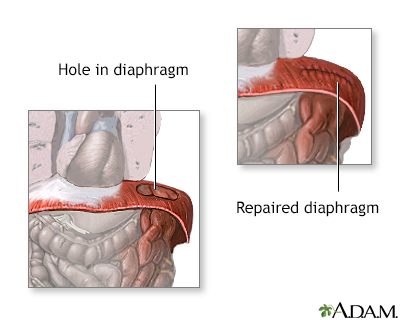
When the diaphragm develops with a hole in it, the abdominal organs can pass into the chest cavity. The lung tissue on the affected side is compressed, fails to grow normally, and is unable to expand after birth. As the child begins to breathe, cry, and swallow, air enters the intestines that are protruding into the chest. The increasing size of the intestines puts pressure on the other side of the chest, lung, and heart and can quickly cause a life-threatening situation.
The indications for a diaphragmatic hernia repair include:
- Chest X-rays showing diaphragmatic hernia
- Severe breathing difficulty (respiratory distress) shortly after birth
- Prenatal ultrasound often identifies a diaphragmatic hernia
|
|
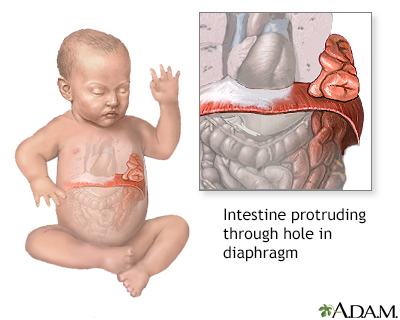
| Procedure, part 1 |
|
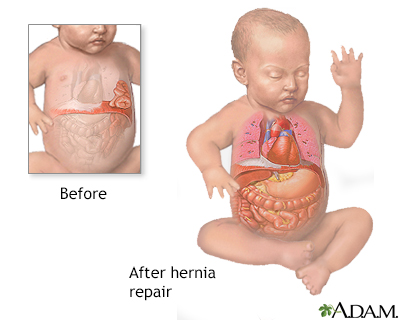
An incision is made in the upper abdomen, under the ribs. The abdominal organs are gently pulled down through the opening in the diaphragm and positioned into the abdominal cavity.
|
|
| Procedure, part 2 |
|
The hole in the diaphragm is repaired and the incision is stitched closed. A tube is placed in the chest to allow air, blood, and fluid to drain so the lung can re-expand.
|
|
| Aftercare |
|
The lung tissue may be underdeveloped on the affected side, and the outcome depends upon the development of the lung tissue. Infants who survive may have some long-term lung disease.
|
|
|
Review Date:
4/6/2025
Reviewed By:
Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. � 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
� 1997-

All rights reserved.