Endometrial ablation
Definition
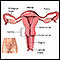
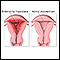
Endometrial ablation is a surgery or procedure done to disrupt the lining of the uterus in order to minimize heavy or prolonged menstrual flow. This lining is called the endometrium. The surgery may be done in a hospital, outpatient surgery center, or the health care provider's office.
Alternative Names
Hysteroscopy - endometrial ablation; Laser thermal ablation; Endometrial ablation - radiofrequency; Endometrial ablation - thermal balloon ablation; Rollerball ablation; Hydrothermal ablation; Novasure ablation
Description
Endometrial ablation is a procedure used to treat abnormal bleeding by destroying tissue in the uterine lining. The tissue can be removed using:
- High frequency radio waves
- Laser energy
- Heated fluids
- Balloon therapy
- Freezing
- Electrical current
Some types of procedures are done using a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope that sends images of the inside of the womb to a video monitor. Most of the time general anesthesia is used so you will be asleep and pain free.
However, newer techniques can be done without using a hysteroscope. For these, a shot of numbing medicine is injected into the nerves around the cervix to block pain.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
This procedure can treat heavy or irregular periods. Your provider will likely have tried other treatments first, such as hormone medicines or an IUD.
Endometrial ablation will not be used if you may want to become pregnant in the future. Though this procedure does not prevent you from getting pregnant, it may reduce your chances of getting pregnant. Reliable contraception is important in all women who get the procedure.
If a woman gets pregnant after an ablation procedure, the pregnancy will often miscarry or be extremely high risk because of the scar tissue in the uterus.
Risks
Risks of hysteroscopy include:
- Hole (perforation) in the wall of the womb
- Scarring of the lining of the womb
- Infection of the uterus
- Damage to the cervix
- Need for surgery to repair damage
- Severe bleeding
- Damage to the bowels
Risks of ablation procedures vary depending on the method used. Risks may include:
- Absorption of excess fluid
- Allergic reaction
- Pain or cramping following the procedure
- Burns or tissue damage from procedures using heat
Risks of any pelvic procedure include:
- Damage to nearby organs or tissues
- Blood clots, which could travel to the lungs and be deadly (rare)
Risks of anesthesia include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Breathing problems
- Lung infection
Risks of any procedure include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
Before the Procedure
A biopsy of the endometrium or lining of the uterus will be performed in the weeks prior to the procedure. Younger women may be treated with a hormone that blocks estrogen from being made by the body for 1 to 3 months before the procedure.
Your provider may prescribe medicine to open your cervix. This makes it easier to insert the scope. You need to take this medicine about 8 to 12 hours before your procedure.
Before the procedure, tell your provider:
- You are or could be pregnant
- You are taking any medicines, including medicines, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription
During the week before your surgery:
- You may be asked to temporarily stop taking medicines that keep your blood from clotting. These medicines are called blood thinners. This includes over-the-counter medicines and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and vitamin E. Many prescription medicines are also blood thinners.
- Ask your provider which medicines you should still take on the day of surgery.
- Tell your provider if you have a cold, flu, fever, herpes outbreak, or other sickness.
- You will be told when to arrive for the procedure. Ask if you need to arrange for someone to drive you home.�
On the day of the procedure:
- Follow instructions about when to stop eating and drinking.
- Take the medicines your surgeon told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
After the Procedure
You may go home the same day. Rarely, you may need to stay overnight.
- You may have menstrual-like cramps and light vaginal bleeding for 1 to 2 days. Ask your provider if you can take over-the-counter pain medicine for the cramping.
- You may have a watery discharge for up to several weeks.
- You can return to normal daily activities within 1 to 2 days. Do not have sex until your provider says it is OK.
- Any biopsy results are usually available within 1 to 2 weeks.
Your provider will tell you the results of your procedure.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The lining of your uterus heals by scarring. Women will most often have less menstrual bleeding after this procedure. Up to 30% to 50% of women will completely stop having periods. This result is more likely in older women. Women who continue to have heavy bleeding may need additional surgery.
References
Baggish MS. Minimally invasive nonhysteroscopic endometrial ablation. In: Baggish MS, Karram MM, eds. Atlas of Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 107.
Kintanar TA. Endometrial ablation. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 133.
Raymond L, Lentz GM. Endoscopy in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 10.
|
Review Date:
10/15/2024 Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |