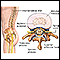
Thoracic spine x-ray
Definition
A thoracic spine x-ray is an x-ray of the 12 chest (thoracic) bones (vertebrae) of the spine. The vertebrae are separated by flat pads of cartilage called disks that provide a cushion between the bones.
Alternative Names
Vertebral radiography; X-ray - spine; Thoracic x-ray; Spine x-ray; Thoracic spine films; Back films
How the Test is Performed
The test is done in a hospital radiology department or in your health care provider's office. You will lie on the x-ray table in different positions. If the x-ray is checking for an injury, care will be taken to prevent further injury.
The x-ray machine will be moved over the thoracic area of the spine. You will hold your breath as the picture is taken so that the picture will not be blurry. Usually, 2 or 3 x-ray views are needed.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider if you are pregnant. Also tell your provider if you have had surgery in your chest, abdomen, or pelvis.
Remove all jewelry and accessories.
How the Test will Feel
The test causes no discomfort. The table may be cold.
Why the Test is Performed
The x-ray helps evaluate:
- Bone injuries
- Cartilage loss
- Arthritis
- Curvature in the spine
- Diseases of the bone
- Tumors of the bone
What Abnormal Results Mean
The test can detect:
- Bone spurs
- Deformities of the spine
- Disk narrowing
- Dislocations
- Fractures (most often compression fractures of the vertebrae)
- Thinning of the bone (osteoporosis)
- Wearing away (degeneration) of the vertebrae
- Abnormal alignment of the bone (spondylolisthesis)
Risks
There is low radiation exposure. X-rays are monitored and regulated to provide the minimum amount of radiation exposure needed to produce the image. Most experts feel that the risk is low compared with the benefits.
Pregnant women and children are more sensitive to the risks of x-rays.
Considerations
The x-ray will not detect problems in the muscles, nerves, and other soft tissues, because these problems cannot be seen well on an x-ray.
References
Preston-Suni K, Kaji AH. Spinal trauma. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 35.
Van Thielen T, van den Hauwe L, Van Goethem JW, Parizel PM. Current status of imaging of the spine and anatomical features. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 47.
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.