Cerebral angiography
Definition
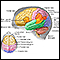
Cerebral angiography is a procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and x-rays to see how blood flows through the brain.
Alternative Names
Vertebral angiogram; Angiography - head; Carotid angiogram; Cervicocerebral catheter-based angiography; Intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography; IADSA
How the Test is Performed
Cerebral angiography is done in the hospital or radiology center.
- You lie on an x-ray table.
- Your head is held still using a strap, tape, or sandbags, so you do not move it during the procedure.
- Before the test starts, you are given a mild sedative to help you relax.
- An electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors your heart activity during the test. Sticky patches, called leads, will be placed on your arms and legs. Wires connect the leads to the ECG machine.
An area of your body, usually the groin or wrist, is cleaned and numbed with a numbing medicine (local anesthetic). A thin, hollow tube called a catheter is placed through an artery. The catheter is carefully moved up through the main blood vessels into an artery in the neck. X-rays help your health care provider (usually a specially trained radiologist) guide the catheter to the correct position.
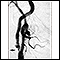
Once the catheter is in place, dye is sent through the catheter. X-ray images are taken to see how the dye moves through the artery and blood vessels of the brain. The dye helps highlight any blockages in blood flow.
Sometimes, a computer removes the bones and tissues on the images being viewed, so that only the blood vessels filled with the dye are seen. This is called digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
After the x-rays are taken, the catheter is withdrawn. Pressure is applied on the leg or wrist at the site of insertion for 10 to 15 minutes to stop the bleeding or a device is used to close the tiny hole. A tight bandage is then applied. Your leg should be kept straight for 2 to 6 hours after the procedure. Watch the area for bleeding for at least the next 12 hours.
Angiography with a catheter is used less often now. This is because magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and CT angiography give clearer images and do not require placing a catheter.
How to Prepare for the Test
Before the procedure, your provider will examine you and may order blood tests.
Tell your provider if you:
- Have a history of bleeding problems or take medicines that are blood thinners
- Have had an allergic reaction to x-ray contrast dye or any iodine substance
- May be pregnant
- Have kidney function problems
You may be told not to eat or drink anything for 4 to 8 hours before the test.
When you arrive at the testing site, you will be given a hospital gown to wear. You must remove all jewelry.
How the Test will Feel
The x-ray table may feel hard and cold. You may ask for a blanket or pillow.
Some people feel a sting when the numbing medicine (anesthetic) is given. You will feel a brief, sharp pain and pressure as the catheter is moved into the body. Once the initial placement is complete, you will not feel the catheter any longer.
The contrast may cause a warm or burning feeling of the skin of the face or head. This is normal and usually goes away within a few seconds.
You may have slight tenderness and bruising at the site of the injection after the test.
Why the Test is Performed
Cerebral angiography is most often used to identify or confirm problems with the blood vessels in or around the brain.
Your provider may order this test if you have symptoms or signs of:
- Abnormal blood vessels in the brain (vascular malformation)
- Bulging blood vessel in the brain (aneurysm)
- Narrowing of the arteries in the brain
- Inflammation of the blood vessels in the brain (vasculitis)
It is sometimes used to:
- Look at blood flow to a tumor.
- Evaluate the arteries of the head and neck before surgery.
- Find a clot that may have caused a stroke.
In some cases, this procedure may be used to get more detailed information after something abnormal has been detected by an MRI or CT scan of the head.
This test may also be done in preparation for medical treatment (interventional radiology procedures) by way of certain blood vessels. For instance, this test can be part of a treatment for a stroke or to treat a brain aneurysm.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Contrast dye flowing out of the blood vessel may be a sign of bleeding.
Narrowed or blocked arteries may suggest:
- Cholesterol deposits
- A spasm of a brain artery
- Inherited disorders
- Blood clots causing a stroke
Out of place blood vessels may be due to:
- Brain tumors
- Bleeding within the skull
- Aneurysm
- Abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain (arteriovenous malformation)
Abnormal results may also be due to cancer that started in another part of the body and has spread to the brain (metastatic brain tumor).
Risks
Complications may include:
- Allergic reaction to the contrast dye
- Blood clot or bleeding where the catheter is inserted, which could partly block blood flow to the leg or hand (rare)
- Damage to an artery or artery wall from the catheter, which can block blood flow and cause a stroke (rare)
- Damage to the kidneys from the IV contrast
Considerations
Tell your provider right away if you have:
- Weakness in your face muscles
- Numbness in your leg during or after the procedure
- Slurred speech during or after the procedure
- Vision problems during or after the procedure
References
Adamczyk P, Liebeskind DS. Vascular imaging: computed tomographic angiography, magnetic resonance angiography, and ultrasound. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 41.
Barras CD, Bhattacharya JJ. Current status of imaging of the brain and anatomical features. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 53.
Reviewed By: Jason Levy, MD, FSIR, Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.