Mononucleosis spot test
Definition
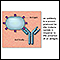
The mononucleosis spot test looks for 2 antibodies in the blood. These antibodies appear during or after an infection with the virus that causes mononucleosis, or mono.
Alternative Names
Monospot test; Heterophile antibody test; Heterophile agglutination test; Paul-Bunnell test; Forssman antibody test
How the Test is Performed
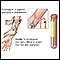
A blood sample is needed.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is necessary.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
The mononucleosis spot test is done when symptoms of mononucleosis are present. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Fever
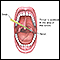
- Large spleen (possibly)
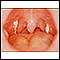
- Sore throat
- Tender lymph nodes along the back of the neck
This test looks for antibodies called heterophile antibodies, which form in the body during the mononucleosis infection.
Normal Results
A negative test means there were no heterophile antibodies detected. Most of the time, this means you do not have infectious mononucleosis.
Sometimes, the test may be negative because it was done too soon (within 1 to 2 weeks) after the illness started. Your health care provider may repeat the test at a later date to make sure you do not have mono.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive test means heterophile antibodies are present. These are most often a sign of mononucleosis. Your provider will also consider other blood test results and your symptoms. A small number of people with mononucleosis may never have a positive test.
The highest number of antibodies occurs 2 to 5 weeks after mono begins. They may be present for up to 1 year.
In rare cases, the test is positive even though you do not have mono. This is called a false-positive result, and it may occur in people with:
- Hepatitis
- Leukemia or lymphoma
- Rubella
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Toxoplasmosis
Risks
Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Johannsen EC, Kaye KM. Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis, Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignant diseases, and other diseases). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 138.
Schooley RD, Allen UD. Epstein-Barr virus infection. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 348.
Stillwell TL, Weinberg JB. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 301.
|
Review Date:
3/16/2024 Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |