Hoarseness
Definition
Hoarseness refers to difficulty making sounds when trying to speak. Vocal sounds may be weak, breathy, scratchy, or husky, and the pitch or quality of the voice may change.
Alternative Names
Voice strain; Dysphonia; Loss of voice
Considerations
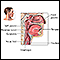
Hoarseness is most often caused by a problem with the vocal cords. The vocal cords are part of your voice box (larynx) located in the throat. When the vocal cords become inflamed or infected, they swell. This can cause hoarseness.
The most common cause of hoarseness is a cold or throat infection, which most often goes away on its own within 2 weeks.
A rare but serious cause of hoarseness that does not go away in a few weeks is cancer of the voice box.
Causes
Hoarseness may be caused by:
- Acid reflux (gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD)
- Allergies
- Breathing in irritating substances
- Cancer of the throat or larynx
- Chronic coughing
- Colds or upper respiratory infections
- Heavy smoking or drinking, particularly together
- Overuse or abuse of the voice (as in shouting or singing), which, over time, may cause swelling or growths on the vocal cords called vocal cord nodules
Less common causes include:
- Injury or irritation from a breathing tube or bronchoscopy
- Damage to the nerves and muscles around the voice box (from trauma or surgery)
- Foreign object in the esophagus or trachea
- Swallowing a harsh chemical liquid
- Changes in the larynx during puberty
- Thyroid or lung cancer
- Underactive thyroid gland
- Immobility of one or both vocal cords
Home Care
Hoarseness may be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic). Vocal rest and time may improve hoarseness. Hoarseness that continues for more than 4 weeks should be checked by a health care provider.
Things you can do at home to help relieve the problem include:
- Talk only when you need to until hoarseness goes away.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help keep your airways moist. (Gargling does not help.)
- Use a vaporizer to add moisture to the air you breathe.
- Avoid actions that strain the vocal cords such as whispering, shouting, crying, and singing.
- Take medicines to reduce stomach acid if hoarseness is due to GERD.
- Do not use decongestants which can dry out the vocal cords.
- If you smoke, cut down, or stop at least until hoarseness goes away.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have trouble breathing or swallowing.
- Hoarseness occurs with drooling, particularly in a small child.
- Hoarseness occurs in a child less than 3 months old.
- Hoarseness has lasted for more than 1 week in a child, or 2 to 3 weeks in an adult.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will examine your throat, neck, and mouth and ask you some questions about your symptoms and medical history. These may include:
- To what extent have you lost your voice (all or partially)?
- What kind of vocal problems are you having (making scratchy, breathy, or husky vocal sounds)?
- When did the hoarseness start?
- Does hoarseness come and go or get worse over time?
- Have you been shouting, singing, or overusing your voice, or crying a lot (if a child)?
- Have you been exposed to harsh fumes or liquids?
- Do you have allergies or a post nasal drip?
- Have you ever had throat surgery?
- Do you smoke or use alcohol?
- Do you have other symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, weight loss, or fatigue?
You may have one or more of the following tests:
- Laryngoscopy
- Throat culture
- Throat examination with a small mirror
- X-rays of the neck or CT scan
- Blood tests such as a complete blood count (CBC) or white blood cell differential
References
Akst L. Hoarseness and laryngitis. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2024. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:28-33.
Bastian RW, Wingo ML. Benign vocal fold mucosal disorders. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 60.
Flint PW. Throat disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 397.
Stachler RJ, Francis DO, Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Hoarseness (Dysphonia) (Update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158(1_suppl):S1-S42. PMID: 29494321 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29494321/.
|
Review Date:
10/28/2024 Reviewed By: Ashutosh Kacker, MD, FACS, Professor of Clinical Otolaryngology, Weill Cornell Medical College, and Attending Otolaryngologist, New York-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |