Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Vaginal hysterectomy; Abdominal hysterectomy; Supracervical hysterectomy; Radical hysterectomy; Removal of the uterus; Laparoscopic hysterectomy; Laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy; LAVH; Total laparoscopic hysterectomy; TLH; Laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy; Robotically assisted hysterectomy DefinitionHysterectomy is surgery to remove a woman's womb (uterus). The uterus is a hollow muscular organ that nourishes the developing baby during pregnancy. DescriptionYou may have all or part of the uterus removed during a hysterectomy. The fallopian tubes and ovaries may also be removed. There are many different ways to perform a hysterectomy. It may be done through:
You and your surgeon will decide which type of procedure. The choice will depend on your medical history and the reason for the surgery. Why the Procedure is PerformedThere are many reasons a woman may need a hysterectomy, including:
Hysterectomy is a major surgery. Some conditions can be treated with medicines or less invasive procedures such as:
RisksRisks of any surgery are:
Risks of a hysterectomy are:
Before the ProcedureBefore deciding to have a hysterectomy, ask your health care provider what to expect after the procedure. Many women notice changes in their body and in how they feel about themselves after a hysterectomy. Talk with your provider, family, and friends about these possible changes before you have surgery. Tell your health care team about all the medicines you are taking. These include herbs, supplements, and other medicines you bought without a prescription. During the days before the surgery:
On the day of your surgery:
After the ProcedureAfter surgery, you will be given pain medicines. You may also have a tube, called a catheter, inserted into your bladder to pass urine. Most of the time, the catheter is removed before leaving the hospital. You will be asked to get up and move around as soon as possible after surgery. This helps prevent blood clots from forming in your legs and speeds recovery. You will be asked to get up to use the bathroom as soon as you are able. You may return to a normal diet as soon as you can without causing nausea and vomiting. How long you stay in the hospital depends on the type of hysterectomy.
Outlook (Prognosis)How long it takes you to recover depends on the type of hysterectomy. Average recovery times are:
A hysterectomy will cause menopause if you also have your ovaries removed. Removal of the ovaries can also lead to a decreased sex drive. Your doctor may recommend estrogen replacement therapy. Discuss with your provider the risks and benefits of this therapy. If the hysterectomy was done for cancer, you may need further treatment. ReferencesCommittee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no 701: choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129(6):e155-e159. PMID: 28538495 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28538495/. Karram MM. Vaginal hysterectomy. In: Baggish MS, Karram MM, eds. Atlas of Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 51. Prescott LS, Yunker AC, Alvarez R. Gynecologic surgery. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 71. Thakar R. Is the uterus a sexual organ? Sexual function following hysterectomy. Sex Med Rev. 2015;3(4):264-278. PMID: 27784599 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27784599/. | ||
| ||
Review Date: 3/31/2024 Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. View References The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | ||


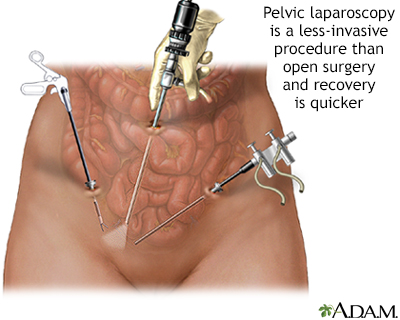 Pelvic laparoscopy
Pelvic laparoscopy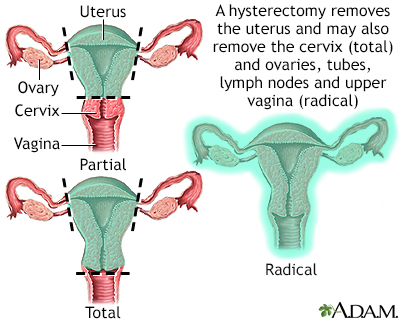 Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy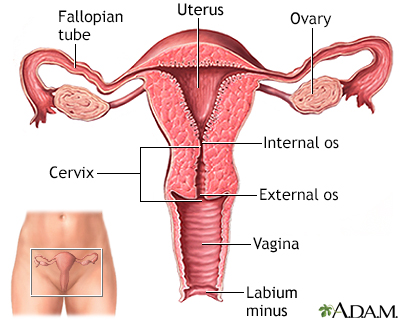 Uterus
Uterus
