Colon cancer screening
Definition
Colon cancer screening can detect polyps and early cancers in the large intestine. This type of screening can find problems that can be treated before cancer develops or spreads. Regular screenings may reduce the risk for death and complications caused by colorectal cancer.
Alternative Names
Screening for colon cancer; Colonoscopy - screening; Sigmoidoscopy - screening; Virtual colonoscopy - screening; Fecal immunochemical test; Stool DNA test; sDNA test; Colorectal cancer - screening; Rectal cancer - screening
Information
SCREENING TESTS
There are several ways to screen for colon cancer.
Stool test:
- Polyps in the colon and small cancers can cause small amounts of bleeding that cannot be seen with the naked eye. But blood can often be found in the stool.
- This method checks your stool for blood.
- A common test used is the fecal immunochemical test (FIT). The fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) was commonly used in the past. Another stool test, commonly known as Cologuard checks for both blood and abnormal stool DNA (sDNA).
Sigmoidoscopy:
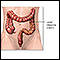
- This test uses a small flexible scope to view the lower part of your colon. Because the test only looks at the last one third of the large intestine (colon), it may miss some cancers or polyps that are higher in the large intestine.
- Sigmoidoscopy and a stool test may be used together.
Colonoscopy:
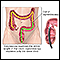
- A colonoscopy is similar to a sigmoidoscopy, but the entire colon can be viewed.
- Your health care provider will give you the steps for cleansing your bowel. This is called bowel preparation.
- During a colonoscopy, you receive medicine to make you relaxed and sleepy.
- Sometimes, CT scans are used as an alternative to a regular colonoscopy. This is called a virtual colonoscopy (or CT colography).
Other test:
- Capsule endoscopy involves swallowing a small, pill-sized camera that takes a video of the inside of your large intestine. The method is being studied, but it is not recommended for standard screening at this time.
SCREENING FOR AVERAGE-RISK PEOPLE
There is not enough evidence to say that any one screening method is best. Colonoscopy is the most thorough but also has the highest risk. Talk to your provider about which test is right for you.
All adults should have a colon cancer screening test starting at age 45.
The most commonly recommended screening options for people with an average risk for colon cancer:
- Colonoscopy every 10 years starting at age 45
- FIT every year (colonoscopy is needed if results are positive)
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years or every 10 years plus stool testing with FIT done every year
Other screening options include the following. If any of these tests are positive, colonoscopy is recommended:
- sDNA-FIT every 3 years
- CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy) every 5 years
SCREENING FOR HIGHER-RISK PEOPLE
People with certain risk factors for colon cancer may need earlier (before age 45) or more frequent testing.
More common risk factors are:
- A family history of inherited colorectal cancer syndromes, such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC).
- A strong family history of colorectal cancer or advanced adenomatous polyps. This usually means close relatives (parent, sibling, or child) who developed these conditions younger than age 60.
- A personal history of colorectal cancer or polyps.
- A personal history of long-term (chronic) inflammatory bowel disease (for example, ulcerative colitis or Crohn disease).
Screening for these groups is more likely to be done using colonoscopy.
References
Garber JJ, Chung DC. Colonic polyps and polyposis syndromes. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 126.
National Cancer Institute website. Colorectal cancer screening (PDQ) -- health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/hp/colorectal-screening-pdq. Updated March 28, 2024. Accessed August 22, 2024.
Patel SG, May FP, Anderson JC, et al. Updates on age to start and stop colorectal cancer screening: Recommendations from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(1):285-299. PMID: 34794816 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34794816/.
Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(7):1016-1030. PMID: 28555630 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28555630/.
Shaukat A, Kahi CJ, Burke CA, Rabeneck L, Sauer BG, Rex DK. ACG Clinical Guidelines: Colorectal cancer screening 2021. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):458-479. PMID: 33657038 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33657038/.
US Preventive Services Task Force; Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for Colorectal Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. PMID: 34003218 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34003218/.
Wolf AMD, Fontham ETH, Church TR, et al. Colorectal cancer screening for average-risk adults: 2018 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(4):250-281. PMID: 29846947 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29846947/.
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.