National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NIH). Activity Calories Burned per Hour.
American Cancer Society. Controlling Portion Sizes. Updated November 16, 2009. Accessed November 10, 2010.
American Heart Association. Quick-Weight-Loss or Fad Diets. Updated May 20, 2010. Accessed November 12, 2010.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 105: bariatric surgery and pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1405-1413.
American Heart Association. Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations. Updated May 21, 2010. Accessed November 12, 2010.
American Heart Association Nutrition Committee, Lichtenstein AH, Appel LJ, Brands M, et al. Diet and lifestyle recommendations revision 2006: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. Circulation. 2006;114:82-96.
The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Clinical Issues Committee. ASMBS Position Statement on Prophylactic Measures to Reduce the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Bariatric Surgery Patients.
Batsis JA, Lopez-Jimenez F, Collazo-Clavell ML, Clark MM, Somers VK, Sarr MG. Quality of life after bariatric surgery: a population-based cohort study. Am J Med. 2009;122:1055.e1-1055.e10.
Livingston EH. Bariatric surgery outcomes at designated centers of excellence vs nondesignated programs. Arch Surg. 2009;144:319-325.
Blackburn GL, Hutter MM, Harvey AM, et al. Expert panel on weight loss surgery: executive report update. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17:842-862.
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, Banel D, Sledge I. Trends in mortality in bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgery. 2007;142:621-632.
Virji A, Murr MM. Caring for patients after bariatric surgery. Am Fam Physician. 2006;73:1403-1408.
Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Overweight and Obesity: Defining Overweight and Obesity. Updated June 21, 2010. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Overweight and Obesity: Causes and Consequences. Updated December 7, 2009. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Overweight and Obesity: Childhood Overweight and Obesity. Updated March 31, 2010. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Healthy Weight: Healthy Eating for a Healthy Weight: Rethink Your Drink. Updated June 5, 2009. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Healthy Weight: Healthy Eating for a Healthy Weight: Cutting Calories. Updated January 27, 2009. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Clinical Issues Committee of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Updated position statement on sleeve gastrectomy as a bariatric procedure. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010;6:1-5.
Fonder MA, Lazarus GS, Cowan DA, Aronson-Cook B, Kohli AR, Mamelak AJ. Treating the chronic wound: A practical approach to the care of nonhealing wounds and wound care dressings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:185-206.
Dale KS, McAuley KA, Taylor RW, et al. Determining optimal approaches for weight maintenance: a randomized controlled trial. CMAJ. 2009;180:E39-E46.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. JAMA. 2010;303:235-241.
Garb J, Welch G, Zagarins S, Kuhn J, Romanelli J. Bariatric surgery for the treatment of morbid obesity: a meta-analysis of weight loss outcomes for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and laparoscopic gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2009;19:1447-1455.
Greenburg DL, Lettieri CJ, Eliasson AH. Effects of surgical weight loss on measures of obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009;122:535-542.
Gowers SG. Management of eating disorders in children and adolescents. Arch Dis Child. 2008;93:331-334.
Leslie D, Kellogg TA, Ikramuddin S. Bariatric surgery primer for the internist: keys to the surgical consultation. Med Clin North Am. 2007;91:353-381.
Livhits M, Mercado C, Yermilov I, et al. Does weight loss immediately before bariatric surgery improve outcomes: a systematic review. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2009;5:713-721.
Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS) Consortium, Flum DR, Belle SH, King WC, et al. Perioperative safety in the longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:445-454.
Mechanick JI, Kushner RF, Sugerman HJ, et al; American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists; Obesity Society; American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Obesity Society, and American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery medical guidelines for clinical practice for the perioperative nutritional, metabolic, and nonsurgical support of the bariatric surgery patient. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17:S1-S70,
White MA, Masheb RM, Rothschild BS, Burke-Martindale CH, Grilo CM. Do patients' unrealistic weight goals have prognostic significance for bariatric surgery? Obes Surg. 2007;17:74-81.
O'Brien PE, Sawyer SM, Laurie C, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in severely obese adolescents: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2010;303:519-526.
Picot J, Jones J, Colquitt JL, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2009;13(41):1-190, 215-357, iii-iv.
Seagle HM, Strain GW, Makris A, Reeves RS, American Dietetic Association. Position of the American Dietetic Association: weight management. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009;109:330-346.
Powers KA, Rehrig ST, Jones DB. Financial impact of obesity and bariatric surgery. Med Clin North Am. 2007;91:321-338.
Pratt JS, Lenders CM, Dionne EA, et al. Best practice updates for pediatric/adolescent weight loss surgery. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17:901-910.
Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Report of the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010. Updated July 13, 2010. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Sacks FM, Bray GA, Carey VJ, et al. Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:859-873.
Solomon H, Liu GY, Alami R, Morton J, Curet MJ. Benefits to patients choosing preoperative weight loss in gastric bypass surgery: new results of a randomized trial. J Am Coll Surg. 2009;208:241-245.
Søvik TT, Taha O, Aasheim ET, et al. Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic duodenal switch for superobesity. Br J Surg. 2010;97:160-166.
LeMont D, Moorhead MK, Parish MS, Reto CS, Ritz SJ. Suggestions for the Pre-Surgical Psychological Assessment of Bariatric Surgery Candidates. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Tarnoff M, Kaplan LM, Shikora S. An evidenced-based assessment of preoperative weight loss in bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2008;18:1059-1061.
Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Healthy Weight: Tips for Parents: Ideas to Help Children Maintain a Healthy Weight. Updated May 19, 2009. Accessed November 12, 2010.
Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders; 2008.
Treadwell JR, Sun F, Schoelles K. Systematic review and meta-analysis of bariatric surgery for pediatric obesity. Ann Surg. 2008;248:763-776.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Your Guide to Choosing Quality Health Care. Accessed November 12, 2010.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.


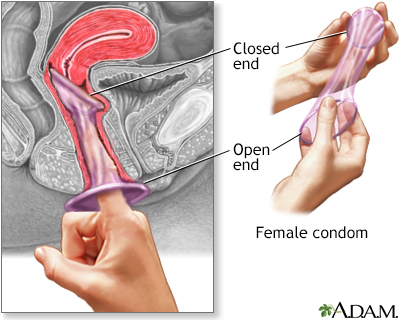 The female condom
The female condom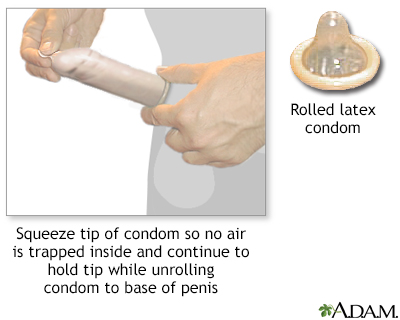 The male condom
The male condom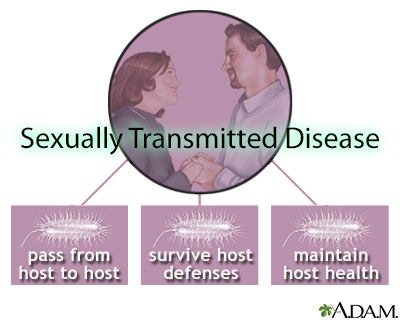 STDs and ecologica...
STDs and ecologica...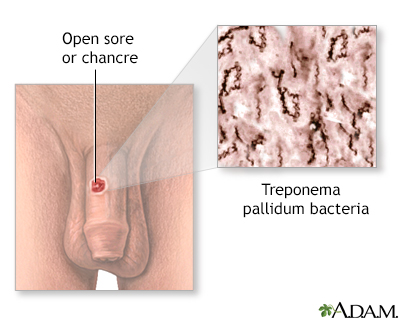 Primary syphilis
Primary syphilis
