Pyogenic granuloma
Definition
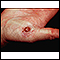
A pyogenic granulomas is a small, raised, and red bump on the skin. The bump has a smooth surface and may be moist. It bleeds easily because of the high number of blood vessels at the site. It is a benign (noncancerous) growth.
Alternative Names
Lobular capillary hemangioma
Causes
The exact cause of pyogenic granulomas is unknown. They often appear following an injury on the hands, arms, or face.
Pyogenic granulomas are common in children and pregnant women.
Symptoms
Signs of a pyogenic granuloma are:
- A small red lump on the skin�that bleeds easily
- Often found at the site of a recent injury
- Usually seen on hands, arms, and face, but�they may develop in the mouth (most often in pregnant women)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will do a physical exam to diagnose this condition.
You may also need a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and check for skin cancer.
Treatment
Small pyogenic granulomas may go away without treatment. If needed, bumps are treated with:
- Surgical shaving or excision
- Electrocautery (heat)
- Freezing
- A laser
- Creams applied to the skin (may not be as effective as surgery)
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most pyogenic granulomas can be removed. A scar may remain after treatment. There is a high chance that the problem will come back if the whole lesion is not removed or destroyed during treatment.
Possible Complications
These problems may occur:
- Bleeding from the lesion
- Return of the condition after treatment
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have a skin bump that bleeds easily or that changes appearance.
References
Dinulos JGH. Vascular tumors and malformations. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 23.
Patterson JW. Vascular tumors. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2021:chap 39.
|
Review Date:
10/14/2024 Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |