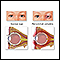
Periorbital cellulitis
Definition
Periorbital cellulitis is an infection of the eyelid or skin around the eye.
Alternative Names
Preseptal cellulitis
Causes
Periorbital cellulitis can occur at any age, but more commonly affects children younger than 5 years old.
This infection can occur after a scratch, injury, or bug bite around the eye, which allows germs to enter the wound. It can also extend from a nearby site that is infected, such as the sinuses.
Periorbital cellulitis is different than orbital cellulitis, which is an infection of the fat and muscles around the eye. In contrast to periorbital cellulitis, orbital cellulitis is a dangerous infection, which can cause lasting problems and deeper infections.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Redness around the eye or in the white part of the eye
- Swelling of the eyelid, whites of eyes, and surrounding area
This condition usually does not affect vision or cause eye pain.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine the eye, especially, eye movements and test for vision, and ask about the symptoms.
Tests that may be ordered include:
Treatment
Antibiotics are given by mouth, by shots, or through a vein (intravenously; IV) to help fight the infection.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Periorbital cellulitis almost always improves with treatment. In rare cases, the infection spreads into the eye socket, resulting in orbital cellulitis.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if:
- The eye becomes red or swollen
- Symptoms get worse after treatment
- Fever develops along with eye symptoms
- It is difficult or painful to move the eye
- The eye looks like it is sticking (bulging) out
- There are vision changes
References
Durand ML. Periocular infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 116.
Olitsky SE, Marsh JD, Jackson MA. Orbital infections. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, ed. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 674.
|
Review Date:
12/31/2023 Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |