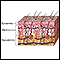
Skin abscess
Definition
A skin abscess is a buildup of pus in or on the skin.
Alternative Names
Abscess - skin; Cutaneous abscess; Subcutaneous abscess; MRSA - abscess; Staph infection - abscess
Causes
Skin abscesses are common and affect people of all ages. They occur when an infection causes pus to collect in the skin.
Skin abscesses may occur after developing:
- A bacterial infection (often staphylococcus)
- A minor wound or injury
- Boils
- Folliculitis (infection in a hair follicle)
A skin abscess may occur anywhere on the body.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Fever or chills, in some cases
- Local swelling around the infected spot
- Hardened skin tissue
- Skin lesion that may be an open or closed sore or a raised area
- Redness, tenderness, and warmth in the area
- Fluid or pus drainage
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can diagnose the problem by looking at the affected area. The drainage from the sore may be sent to the lab for a culture. This can help identify the cause of the infection.
Treatment
You can apply moist heat (such as warm compresses) to help the abscess drain and heal faster. Do not push and squeeze on the abscess.
Your provider may cut open the abscess and drain it. If this is done:
- Numbing medicine will be put on or into your skin.
- Packing material may be left in the wound to help it heal.
You may need to take antibiotics by mouth to control the infection.
If you have methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or another staph infection, follow instructions for self-care at home.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most skin abscesses can be cured with proper treatment. Infections caused by MRSA respond to specific antibiotics.
Possible Complications
Complications that can occur from an abscess include:
- Spread of the infection in the same area
- Spread of the infection into the blood and throughout the body
- Tissue death (gangrene)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have any signs of skin infection, including:
- Drainage of any kind
- Fever
- Pain
- Redness
- Swelling
Contact your provider right away if you develop new symptoms during or after treatment of a skin abscess.
Prevention
Keep the skin around minor wounds clean and dry to prevent infection. Call your provider if you notice signs of infection. Take care of minor infections promptly.
References
Ambrose G, Berlin D. Incision and drainage. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 37.
Dinulos JGH. Bacterial infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
McLarney RM, Sommer LL, Reboli AC, Heymann WR. Bacterial diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 74.
Que Y-A, Moreillon P. Staphylococcus aureus (including staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 194.
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.