Actinic keratosis
Definition
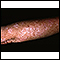
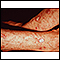
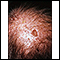
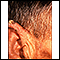
Actinic keratosis is a small, rough, raised area on your skin. Often this area has been exposed to the sun over a long period of time.
Some actinic keratoses may develop into a type of skin cancer.
Alternative Names
Solar keratosis; Sun-induced skin changes - keratosis; Keratosis - actinic (solar); Skin lesion - actinic keratosis
Causes
Actinic keratosis is caused by exposure to sunlight.
You are more likely to develop it if you:
- Have fair skin, blue or green eyes, or blond or red hair
- Had a kidney or other organ transplant
- Take medicines that suppress the immune system
- Spend a lot of time each day in the sun (for example, if you work outdoors)
- Had many severe sunburns early in life
- Are older
Symptoms
Actinic keratosis is usually found on the face, scalp, back of the hands, chest, or places that are often in the sun.
- The skin changes begin as flat and scaly areas. They often have a white or yellow crusty scale on top.
- The growths may be gray, pink, red, or the same color as your skin. Later, they may become hard and wart-like or gritty and rough.
- The affected areas may be easier to feel than see.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will look at your skin to diagnose this condition. A skin biopsy may be done to see if it is cancer.
Treatment
Some actinic keratoses become squamous cell skin cancer. Have your provider look at all skin growths as soon as you find them. Your provider will tell you how to treat them.
Growths may be removed by:
- Burning (electrical cautery)
- Scraping away the lesion and using electricity to kill any remaining cells (called curettage and electrodesiccation)
- Cutting the tumor out and using stitches to place the skin back together (called excision)
- Freezing (cryotherapy, which freezes and kills the cells)
If you have many of these skin growths, your provider may recommend:
- A special light treatment called photodynamic therapy
- Chemical peels
- Skin creams, such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and imiquimod
Outlook (Prognosis)
A small number of these skin growths turn into squamous cell carcinoma.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you see or feel a rough or scaly spot on your skin, or if you notice any other skin changes.
Prevention
The best way to lower your risk for actinic keratosis and skin cancer is to learn how to protect your skin from sun and ultraviolet (UV) light.
Things you can do to lower your exposure to sunlight include:
- Wear clothing such as hats, long-sleeved shirts, long skirts, or pants.
- Try to avoid being in the sun during midday, when ultraviolet light is most intense.
- Use high-quality sunscreens, preferably with a sun protection factor (SPF) rating of at least 30. Pick a broad-spectrum sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB light.
- Apply sunscreen before going out into the sun, and reapply often -- at least every 2 hours while in the sun.
- Use sunscreen year-round, including in the winter.
- Avoid sun lamps, tanning beds, and tanning salons.
Other things to know about sun exposure:
- Sun exposure is stronger in or near surfaces that reflect light, such as water, sand, snow, concrete, and areas painted white.
- Sunlight is more intense at the beginning of the summer.
- Skin burns faster at higher altitudes.
References
American Academy of Dermatology Association website. Actinic keratosis: diagnosis and treatment. www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/actinic-keratosis-treatment. Updated February 23, 2022. Accessed October 22, 2024.
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Skin, hair, and nails. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 9.
Dinulos JGH. Premalignant and malignant nonmelanoma skin tumors. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 21.
Wolf IH, Soyer HP, McMeniman EK, Wolf P. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 108.
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.