Femoral nerve dysfunction
Definition
Femoral nerve dysfunction is a loss of movement or sensation in parts of the legs due to damage to the femoral nerve.
Alternative Names
Neuropathy - femoral nerve; Femoral neuropathy
Causes
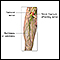
The femoral nerve is located in the pelvis and goes down the front of the leg. It helps the muscles move the hip and straighten the leg. It provides feeling (sensation) to the front of the thigh and part of the lower leg.
A nerve is made up of many fibers, called axons, surrounded by insulation, called the myelin sheath.
Damage to any one nerve, such as the femoral nerve, is called mononeuropathy. Mononeuropathy is usually due to a local cause of damage to a single nerve. Disorders that involve the entire body (systemic disorders) can also cause isolated nerve damage to one nerve at a time (such as occurs with mononeuritis multiplex).
More common causes of femoral nerve dysfunction are:
- Direct injury (trauma)
- Prolonged pressure on the nerve
- Compression, stretching, or entrapment of the nerve by nearby parts of the body or disease-related structures (such as a tumor or abnormal blood vessel)
The femoral nerve can also be damaged from any of the following:
- A broken pelvis bone
- A catheter placed into the femoral artery in the groin
- Diabetes or other causes of peripheral neuropathy
- Internal bleeding in the pelvis or belly area (abdomen)
- Lying on the back with the thighs and legs flexed and turned (lithotomy position) during surgery or diagnostic procedures
- Tight or heavy waist belts
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Sensation changes in the thigh, knee, or leg, such as decreased sensation, numbness, tingling, burning, or pain
- Weakness of the knee or leg, including difficulty going up and down stairs -- especially down, with a feeling of the knee giving way or buckling
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will ask about your symptoms and examine you. This will include an exam of the nerves and muscles in your legs.
The exam may show that you have:
- Weakness when you straighten the knee or bend at the hip
- Sensation changes at the front of the thigh or in the foreleg
- An abnormal knee reflex
- Smaller than normal quadriceps muscles on the front of the thigh
Tests that may be done include:
- Electromyography (EMG) to check the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
- Nerve conduction (NCV) tests to check how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is usually done at the same time as an EMG.
- MRI or CT scan to check for masses or tumors.
Your provider may order additional tests, depending on your medical history and symptoms. Tests may include blood tests, x-rays, and other imaging tests.
Treatment
Your provider will try to identify and treat the cause of the nerve damage. You'll be treated for any medical problems (such as diabetes or bleeding in the pelvis) that may be causing the nerve damage. In some cases, the nerve will heal with treatment of the underlying medical problem.
Other treatments may include:
- Surgery to remove a tumor or growth that is pressing on the nerve
- Medicines to relieve pain
- Weight loss and change in lifestyle if diabetes or excess weight is contributing to the nerve damage
In some cases, no treatment is needed and you'll recover on your own. If so, any treatment, such as physical therapy and occupational therapy, is aimed at increasing mobility, maintaining muscle strength, and independence while you recover. Braces or splints may be prescribed to help in walking.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the cause of the femoral nerve dysfunction can be identified and successfully treated, it is possible to recover fully. In some cases, there may be partial or complete loss of movement or sensation, resulting in some degree of permanent disability.
Nerve pain may be uncomfortable and can continue for a long time. Injury to the femoral area may also injure the femoral artery or vein, which can cause bleeding and other problems.
Possible Complications
Complications that may result include:
- Repeated injury to the leg that goes unnoticed due to loss of sensation
- Injury from falls due to muscle weakness
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of femoral nerve dysfunction.
References
Clinchot DM, Craig EJ. Femoral neuropathy. In: Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD Jr, eds. Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 54.
Katirji B. Disorders of peripheral nerves. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff’s Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 106.
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.