| Weight loss glossary |
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
|
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
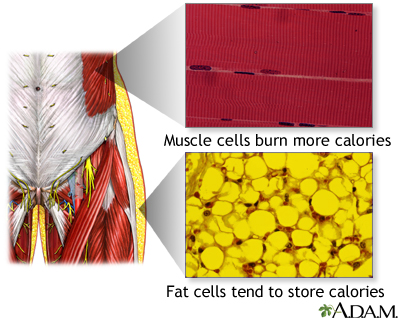
Adipose tissue: Fat tissue in the body.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Bariatric surgery: Surgery on the stomach and intestines to help the patient with extreme obesity lose weight. Bariatric surgery is a weight-loss method used for people who have a body mass index (BMI) above 40. Surgery may also be an option for people with a BMI between 35 and 40 who have health problems like heart disease or type 2 diabetes.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA): A way to estimate the amount of body weight that is fat and nonfat. Nonfat weight comes from bone, muscle, body water, organs, and other body tissues. BIA works by measuring how difficult it is for a harmless electrical current to move through the body. The more fat a person has, the harder it is for electricity to flow through the body. The less fat a person has, the easier it is for electricity to flow through the body. By measuring the flow of electricity, one can estimate body fat percent.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Body mass index (BMI): A measure of body weight relative to height. BMI can be used to determine if people are at a healthy weight, overweight, or obese. A body mass index (BMI) of 18.5 - 25 refers to a healthy weight, a BMI of 25 - 30 refers to overweight. A BMI of 30 or higher refers to obese.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
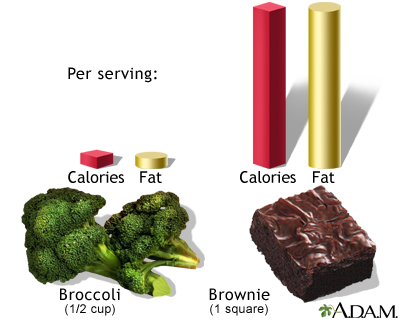
Calorie: A unit of energy in food. Foods have carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Some beverages have alcohol. Carbohydrates have 4 calories per gram. Proteins have 4 calories per gram. Alcohol has 7 calories per gram. Fat has 9 calories per gram.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Carbohydrate: A major source of energy in the diet. There are two kinds of carbohydrates -- simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates are sugars and complex carbohydrates include both starches and fiber. Carbohydrates have 4 calories per gram. They are found naturally in foods such as breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Foods such as sugar cereals, soft drinks, fruit drinks, fruit punch, lemonade, cakes, cookies, pies, ice cream, and candy are very rich in sugars.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Diet: What a person eats and drinks. Any type of eating plan.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Energy expenditure: The amount of energy, measured in calories, that a person uses. Calories are used by people to breathe, circulate blood, digest food, and be physically active.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
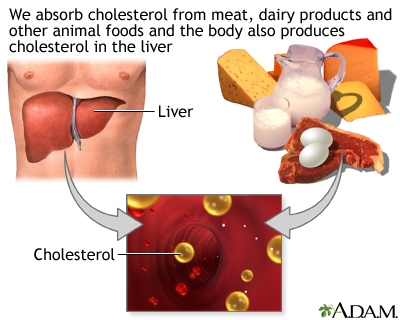
Fat: A major source of energy in the diet. All food fats have 9 calories per gram. Fat helps the body absorb fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, and carotenoids. Some kinds of fats, especially saturated fats, may cause blood cholesterol to increase and increase the risk for heart disease. Other fats, such as unsaturated fats, do not increase blood cholesterol. Fats that are in foods are combinations of monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and saturated fatty acids.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
HDL: See high-density lipoprotein.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Healthy weight: Compared to overweight or obese, a body weight that is less likely to be linked with any weight-related health problems such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, or others. A body mass index (BMI) of 18.5 - 25 refers to a healthy weight, though not all individuals with a BMI in this range may be at a healthy level of body fat; they may have more body fat tissue and less muscle. A BMI of 25 - 30 is considered overweight, and a BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
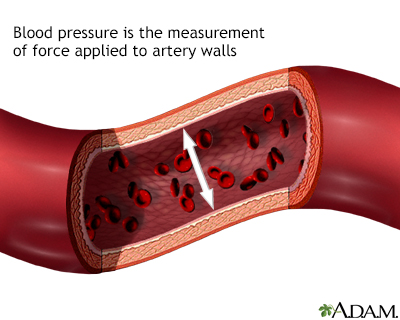
High blood pressure: Another word for "hypertension." Blood pressure rises and falls throughout the day. An optimal blood pressure is less than 120/80 mmHg. When blood pressure stays high, greater than or equal to 140/90 mmHg, then it is considered high blood pressure. High blood pressure increases the risk for heart disease and stroke.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
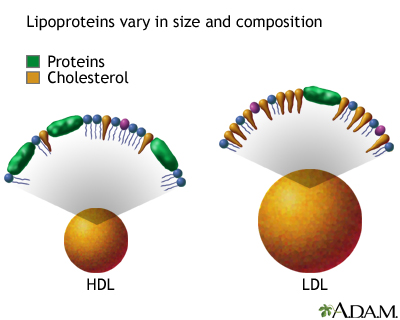
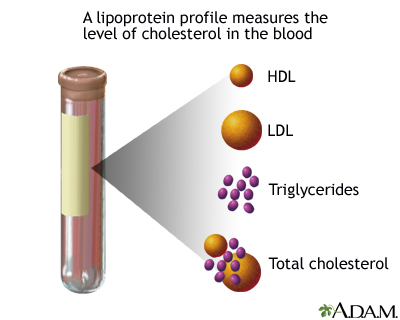
High-density lipoprotein (HDL): A form of cholesterol that circulates in the blood. Commonly called "good" cholesterol. High HDL lowers the risk of heart disease. An HDL of 60 mg/dl or greater is considered high and is protective against heart disease. An HDL less than 40 mg/dl is considered low and increases the risk for developing heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Hydrogenation: A chemical way to turn liquid fat (oil) into solid fat. This process creates a fat called trans fatty acid. Trans fatty acids are found in margarine, shortening, and some commercial baked foods like cookies, crackers, muffins, and cereals. Eating a large amount of trans fatty acids may raise heart disease risk.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Kcal: The abbreviation for "Kilocalories," a unit of energy. This is equivalent to the unit of energy known as a Calorie (which is generally not capitalized in common usage).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
LDL: See low-density lipoprotein.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Lipoprotein: Compounds of protein that carry fats and fat-like substances, such as cholesterol, in the blood.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): A form of cholesterol that circulates in the blood. Commonly called "bad" cholesterol. High LDL increases the risk of heart disease. An LDL less than 100 mg/dl is considered optimal, 100 - 129 mg/dl is considered near or above optimal, 130 - 159 mg/dl is considered borderline high, 160 - 189 mg/dl is considered high, and 190 mg/dl or greater is considered very high.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Metabolism: All of the processes that occur in the body that turn the food you eat into energy your body can use.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Monounsaturated fat: Fats that are in foods are combinations of monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and saturated fatty acids. Monounsaturated fat is found in canola oil, olives and olive oil, nuts, seeds, and avocados. Eating food that has more monounsaturated fat instead of saturated fat may help lower cholesterol and reduce heart disease risk. However, it has the same number of calories as other types of fat, and may still contribute to weight gain if eaten in excess.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Obesity: Having a high amount of body fat. A person is considered obese if he or she has a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Overweight: Being too heavy for one's height. It is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 25 - 30. Body weight comes from fat, muscle, bone, and body water. Overweight does not always mean over fat.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Percent body fat: A measurement of how much of your body weight is due to fat versus muscle and other tissues. Percent body fat can be a good indicator of how overweight you are and the potential impact of your weight on your health. However, there is no easy way to measure this at home. For most purposes, other methods like body mass index, waist circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio are sufficient for determining whether you are overweight. Percent body fat can be determined with calipers that measure a fold of skin, water displacement, or bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Physical activity: Any form of exercise or movement. Physical activity may include planned activity such as walking, running, basketball, or other sports. Physical activity may also include other daily activities such as household chores, yard work, walking the dog, etc.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Polyunsaturated fat: A highly unsaturated fat that is liquid at room temperature. Fats that are in foods are combinations of monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and saturated fatty acids. Polyunsaturated fats are found in greatest amounts in corn, soybean, and safflower oils, and many types of nuts. They have the same number of calories as other types of fat, and may still contribute to weight gain if eaten in excess.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Protein: One of the three nutrients that provides calories to the body. Protein is an essential nutrient that helps build many parts of the body, including muscle, bone, skin, and blood. Protein provides 4 calories per gram and is found in foods like meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, beans, nuts, and tofu.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Registered Dietitian (R.D.): A health professional who is a food and nutrition expert. A person who has studied diet and nutrition at an American Dietetic Association (ADA) approved college program and passed an exam to become a registered dietitian.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Saturated fat: A fat that is solid at room temperature. Fats that are in foods are combinations of monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and saturated fatty acids. Saturated fat is found in high-fat dairy products (like cheese, whole milk, cream, butter, and regular ice cream), fatty fresh and processed meats, the skin and fat of chicken and turkey, lard, palm oil, and coconut oil. They have the same number of calories as other types of fat, and may contribute to weight gain if eaten in excess. Eating a diet high in saturated fat also raises blood cholesterol and risk of heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Trans fatty acids: A fat that is produced when liquid fat (oil) is turned into solid fat through a chemical process called hydrogenation. Eating a large amount of trans fatty acids also raises blood cholesterol and risk of heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Underwater weighing: A research method for estimating body fat. A person is placed in a tank, underwater, and weighed. By comparing weight underwater with weight on land, one can get a very good measure of body fat.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Unsaturated fat: A fat that is liquid at room temperature. Vegetable oils are unsaturated fats. Unsaturated fats include polyunsaturated fats and monounsaturated fats. They include most nuts, olives, avocados, and fatty fish, like salmon.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Very-low calorie diet: A person following a VLCD eats or drinks a commercially prepared formula that has 800 calories or less, instead of eating food. A VLCD can allow a person to lose weight more quickly than is usually possible with low-calorie diets, but should only be used under the supervision of a health care provider.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
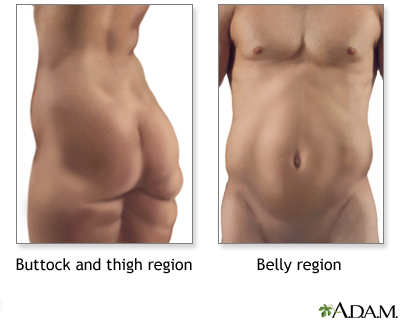
Waist circumference: A measurement of the waist. Fat around the waist increases the risk of obesity-related health problems. Women with a waist measurement of more than 35 inches or men with a waist measurement of more than 40 inches have a higher risk of developing obesity-related health problems, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Weight control: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight by eating well and getting regular physical activity.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Yo-yo dieting: Losing and gaining weight over and over again.

|
Review Date:
6/28/2011 Reviewed By: Jeffrey Heit, MD, Internist with special emphasis on preventive health, fitness and nutrition, Philadelphia VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc. |