| Drug treatment - NSAIDs |
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are the most commonly used type of medication for back pain. They work by blocking a substance called prostaglandin. Normally, prostaglandins dilate blood vessels (leading to increased blood flow) and promote inflammation, both of which can contribute to pain. By stopping the usual actions of prostaglandins, NSAIDs help reduce pain and inflammation.
Types of NSAIDs
NSAIDs are available over-the-counter or by prescription. They are either seletive or non-selective. The prescription versions are generally stronger and last longer.
Non-selective NSAIDs include:
- Aspirin
- Diclofenac (Voltaren)
- Etodolac (Lodine)
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, Motrin IB, Nuprin)
- Indomethacin (Indocin)
- Ketoprofen (Orudis, Oruvail)
- Nabumetone (Relafan)
- Naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprosyn)
- Piroxicam (Feldene)
- Salsalate (Disalcid)
- Sulindac (Clinoril)
- Tolemetin (Tolectin)
Selective NSAIDs include:
- COX-2 Inhibitors, such as celecoxib (Celebrex)
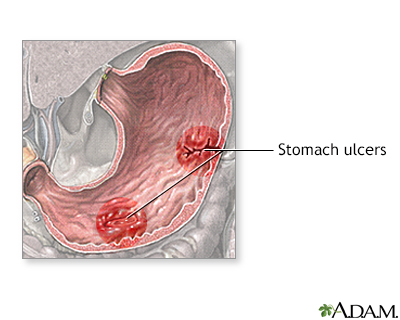
Risk of ulcers and GI bleeding
Regular use of non-selective NSAIDs, especially long-term use, can have serious complications like ulcers, bleeding from your gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and kidney damage. (Selective COX-2 inhibitors, however, may be associated with a lower risk of ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding.) You are at particular risk of developing ulcers from these drugs (including bleeding ulcers) if you:
- Are over age 60
- Have had an ulcer in the past or history of bleeding from your GI tract
- Drink alcohol on a regular basis
- Take certain medications, such as warfarin (Coumadin), steroids, or alendronate (Fosamax)
Other possible side effects
NSAIDs can cause or worsen the following conditions:
- Cardiovascular: Evidence from large research trials has showed increased rates of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events and heart attacks in patients taking NSAIDs.
- High blood pressure: NSAIDs can increase blood pressure. If you have high blood pressure, check with your doctor before using NSAIDs, especially if you take blood pressure lowering medication.
- Kidney disease: NSAIDs can cause kidney damage. If you already have any type of kidney disease, don't use NSAIDs. If while taking an NSAID, you develop sudden weight gain or fluid retention (for example, you notice swelling in your legs), notify your doctor right away.
- Diabetes: NSAIDs can cause a change in blood sugar. Check with your doctor before using NSAIDs if you have diabetes. You may still be able to use them, but you may need to follow your blood sugars closely and, with the help of your doctor, adjust your diabetes medications appropriately.
Finally, NSAIDs can cause:
- Dizziness
- Tinnitus (ringing in your ear)
- Headache
- Skin rash
- Confusion
Reviewed By: Andrew W. Piasecki, MD, Camden Bone and Joint, LLC, Orthopaedic Surgery/Sports Medicine, Camden, SC. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
