| Exercise glossary |
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
|
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Aerobic: Relating to oxygen and its use in the body.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Aerobic exercise: Also called cardiovascular exercise, this type of exercise builds endurance by keeping the heart pumping for an extended period of time. It strengthens your heart and blood vessels, improves cholesterol, strengthens bones, and helps you lose weight.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Aerobics: A type of cardiovascular exercise that involves repeated body movements, such as stepping and bending, often to music.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
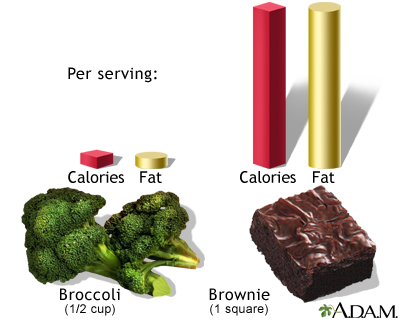
Calorie: A unit of energy provided by food that is used by the body. Two different foods of equal weight provide a different number of calories. (For example, a gram of broccoli has fewer calories than a gram of brownie.) High-calorie foods are more likely to cause your body to store unnecessary calories as fat in the body, because the extra calories are not burned off by muscle activity and metabolism.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cardiac: Relating to the heart.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cardiovascular exercise: Also called aerobic exercise, this type of exercise builds endurance by keeping the heart pumping for an extended period of time. It strengthens your heart and blood vessels, improves cholesterol, strengthens bones, and helps you lose weight.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Carotid pulse: The heartbeat you can feel by placing two fingers lightly under the angle of your jaw.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Concentric contractions: These movements shorten muscles (for example, the "up" motion when a bicep lifts a weight).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Cool down: The final period of your workout where you slow the pace of your activity and gradually bring your heart and breathing rate back to normal. If you don't cool down, your blood pressure may drop too quickly, which can cause dizziness or lightheadedness. It may also trigger abnormal rhythms of the heart, which are extremely dangerous.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Eccentric contractions: These movements lengthen muscles (the "down" phase as weights are lowered).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
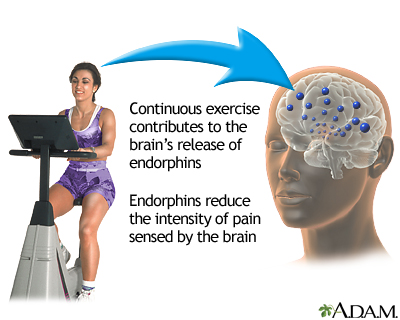
Endorphins: Hormones released by your brain during exercise that make you feel good. This can help you enjoy the exercise and may improve your mood for several hours after your workout.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Endurance: The length of time your body is physically able to perform an exercise. For example, when you begin running, you may be able to run for only a few minutes, but gradually your endurance may increase until you can run much longer times.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Exercise: Physical activity that is usually performed with a fairly regular workout routine, often to meet specific fitness goals.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Fatigue: A lack of energy or a feeling of being tired following exercise, physical exertion, and insufficient calorie intake. (There are also medical causes.)
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Flexibility training: These exercises help your muscles stretch farther in a given direction. Flexibility training helps prevent cramps, stiffness, and injuries, and can give you a wider range of motion. These exercises also emphasize proper breathing, balance, and alignment. Some forms of flexibility training, such as yoga, pilates, and tai chi, include meditation and breathing techniques that can reduce stress.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Heart rate: The number of times your heart beats within a minute. Each individual beat can be felt in certain locations on the body. (See carotid pulse and radial pulse.) You can count these beats to calculate your heart rate (beats per minute).
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Isometric exercise: An exercise that does not change the length of the muscle. For example, pushing against a wall.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
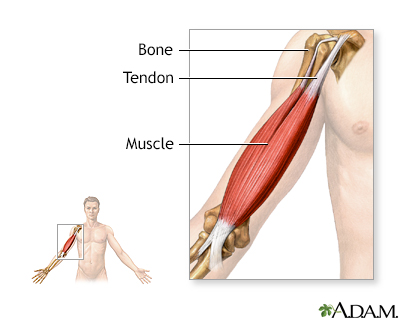
Ligament: Tissue that connects one bone to another bone.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Maximum heart rate: The fastest your heart can beat, no matter how hard you exercise. The most accurate way to measure this is with an exercise stress test. While you walk or run on a treadmill, measurements of your blood pressure and heart rate are recorded. A less exact way to determine your maximum heart rate is with a simple calculation based on your age. (Subtract your age from 220.)
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Metabolism: All of the biochemical processes in the body that use energy throughout the day, including digestion, production of hormones, breathing, and regulation of body temperature.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Physical activity: Any body movement that burns more calories than a state of physical rest. In addition to exercises like running or lifting weights, physical activity includes countless non-structured activities like gardening and getting up to turn off the TV.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Radial pulse: The heartbeat you can feel by placing two fingers lightly on the wrist, just under the thumb.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Reps: Short for "repetitions," which is the number of times you perform an exercise without stopping. For example, each time you lift a weight and then lower it again is one repetition. If you lift the weight and then lower it ten times and then stop, you have done a "set" consisting of 10 reps.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
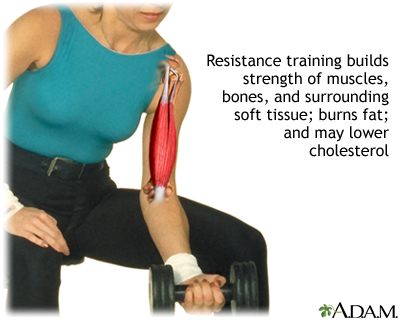
Resistance training: See weight training.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Resting heart rate: Your heart rate while you are not exerting yourself.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Set: A group of repetitions. A set is usually followed by a brief period of rest or alternate exercise, after which you do another set, and repeat until done.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Spot reducing: An ineffective exercise strategy that focuses on one body part with the goal of losing fat in that one area. However, fat is not lost in targeted locations just because muscles in that area are exercised. When you burn excess calories, fat is lost all over the body. Therefore, an hour of brisk walking on a regular basis would be more effective at losing extra weight in your stomach area than doing 20 situps every day.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Strength training: See weight training.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Stress Test: A stress test helps determine the risk for a heart attack from exercise. Anyone with a heart problem or history of heart disease should have a stress test before embarking on an exercise program. Many experts currently also recommend this test before a vigorous exercise program for older persons who are sedentary, even in the absence of known or suspected cardiovascular disease. It is expensive, however, and some experts believe that it may not be necessary for many older people with no evident health problems or risk factors. They recommend instead a carefully monitored program, starting out with low-intensity exercises and gradually building up.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Stretching: Applying gentle pressure to a muscle, generally after a workout when the muscles are warm, to help the muscle heal and increase flexibility.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Target heart rate: When your heart is beating between 60 - 80% of its maximum rate.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Tendon: Tissue that connects muscle to bone.
Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Warm up: Any simple, comfortable movement that lets your body gradually adjust from a resting state to the demands of intense exercise. The warm-up is performed at the start of exercise. Most people find it convenient to warm up by doing their chosen activity at a slower pace. Warming up helps you avoid injuring your muscles and straining your heart.

Click a word on the left and the definition will appear here:
Weight training: Also called strength or resistance training, these exercises build up your muscles and help maintain bone density. Strength training involves performing repetitions ("reps") that move specific muscles in the same pattern repeatedly against a resisting force.
|
Review Date:
6/28/2011 Reviewed By: Jeffrey Heit, MD, Internist with special emphasis on preventive health, fitness and nutrition, Philadelphia VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc. |