Esophageal cancer
Definition
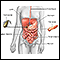
Esophageal cancer is cancer that starts in the esophagus. This is the tube through which food moves from the mouth to the stomach.
Alternative Names
Cancer - esophagus
Causes
Esophageal cancer is not common in the United States. It occurs most often in men over age 50 years.
There are two main types of esophageal cancer, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. These two types look different from each other under the microscope.
Squamous cell esophageal cancer is linked to smoking and drinking too much alcohol.
Adenocarcinoma is the more common type of esophageal cancer. Having Barrett esophagus increases the risk for this type of cancer. Acid reflux disease (gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD) can develop into Barrett esophagus. Other risk factors include smoking, being male, or being obese.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Backward movement of food through the esophagus and possibly mouth (regurgitation)
- Chest pain not related to eating
- Difficulty swallowing solids or liquids
- Heartburn
- Vomiting blood
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
Tests used to help diagnose esophageal cancer may include:
- Series of x-rays taken to examine the esophagus (barium swallow)
- Chest MRI or thoracic CT (usually used to help determine the stage of the disease)
- Endoscopic ultrasound (also sometimes used to determine the stage of disease)
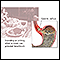
- Examining and removing a sample of the lining of the esophagus (esophagogastroduodenoscopy, EGD)
- PET scan (sometimes useful for determining the stage of disease, and whether surgery is possible)
Stool testing may show small amounts of blood in the stool.
Treatment
EGD will be used to obtain a tissue sample from the esophagus to diagnose cancer.
When the cancer is only in the esophagus and has not spread, surgery may be done. The cancer and part, or all, of the esophagus is removed. The surgery may be done using:
- Open surgery, during which 1 or 2 large incisions are made.
- Minimally invasive surgery, during which 2 to 4 small incisions are made in the belly. A laparoscope with a tiny camera is inserted into the belly through one of the incisions.
Radiation therapy may also be used instead of surgery in some cases when the cancer has not spread outside the esophagus.
Either chemotherapy, radiation, or both may be used to shrink the tumor and make surgery easier to perform.
If the person is too ill to have major surgery or the cancer has spread to other organs, chemotherapy or radiation may be used to help reduce symptoms. This is called palliative therapy. In such cases, the disease is usually not curable.
Besides a change in diet, other treatments that may be used to help the person swallow include:
- Dilating (widening) the esophagus using an endoscope. Sometimes a stent is placed to keep the esophagus open.
- A feeding tube into the stomach.
- Photodynamic therapy, in which a special medicine is injected into the tumor and is then exposed to light. The light activates the medicine that attacks the tumor.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Outlook (Prognosis)
When the cancer has not spread outside the esophagus, surgery may improve the chance of survival.
When the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, a cure is generally not possible. Treatment is directed toward relieving symptoms.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Pneumonia
- Severe weight loss from not eating enough
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have difficulty swallowing with no known cause and it does not get better. Also contact your provider if you have other symptoms of esophageal cancer.
Prevention
To reduce your risk of cancer of the esophagus:
- Do not smoke.
- Limit or do not drink alcoholic beverages.
- Get checked by your provider if you have severe GERD.
- Get regular endoscopies as recommended by your provider if you have Barrett esophagus.
References
Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Bentrem DJ. Esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancers, version 2.2023, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21(4): 393-422. PMID: 37015332 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37015332/.
Ku GY, Ilson DH. Cancer of the esophagus. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 71.
National Cancer Institute website. Esophageal cancer treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/esophageal/hp/esophageal-treatment-pdq. Updated March 21, 2025. Accessed July 28, 2025.
Reviewed By: Todd Eisner, MD, Private practice specializing in Gastroenterology in Boca Raton and Delray Beach, Florida at Gastroenterology Consultants of Boca Raton. Affiliate Assistant Professor, Florida Atlantic University School of Medicine. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.