Pregnancy SmartSiteTM
Food poisoning - campylobacter enteritis; Infectious diarrhea - campylobacter enteritis; Bacterial diarrhea; Campy; Gastroenteritis - campylobacter; Colitis - campylobacter DefinitionCampylobacter infection occurs in the small intestine from bacteria called Campylobacter jejuni. It is a type of bacterial food poisoning. CausesCampylobacter enteritis is a common cause of intestinal infection. These bacteria are also one of the many causes of traveler's diarrhea or food poisoning. People most often get infected by eating or drinking food or water that contains the bacteria. The most commonly contaminated foods are raw poultry, fresh produce, and unpasteurized milk. A person can also be infected by close contact with infected people or animals. SymptomsSymptoms start 2 to 4 days after being exposed to the bacteria. They often last a week, and may include:
Exams and TestsYour health care provider will perform a physical exam. These tests may be done:
TreatmentThe infection almost always goes away on its own, and often does not need to be treated with antibiotics. Severe symptoms may improve with antibiotics. The goal is to make you feel better and avoid dehydration. Dehydration is a loss of water and other fluids in the body. These things may help you feel better if you have diarrhea:
People who take diuretics ("water pills") may need to stop taking these medicines if they have acute Camplyobacter enteritis. Never stop taking any medicine without first talking to your provider. Outlook (Prognosis)Most people recover in 5 to 8 days. When a person's immune system does not work well, the Campylobacter infection may spread to the heart or brain. Other problems that may occur are:
When to Contact a Medical ProfessionalContact your provider if:
Contact your provider if your child has:
PreventionLearning how to prevent food poisoning can reduce the risk for this infection. ReferencesAllos BM. Campylobacter infections. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 279. Allos BM, Blaser MJ, Iovine NM, Kirkpatrick BD. Campylobacter jejuni and related species. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 216. Fleckenstein JM. Approach to the patient with suspected enteric infection. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 262. Hammershaimb EA, Kotloff KL . Acute gastroenteritis in children. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 387. Lima AAM, Warren CA, Guerrant RL. Acute dysentery syndromes (diarrhea with fever). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 99. Melia JMP, Sears CL. Infectious enteritis and proctocolitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 110. | ||
| ||
Review Date: 3/16/2024 Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. View References The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. | ||


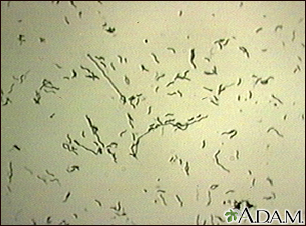 Campylobacter jeju...
Campylobacter jeju...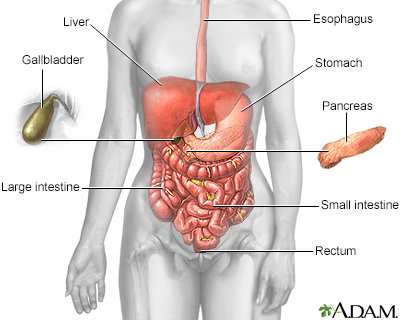 Digestive system
Digestive system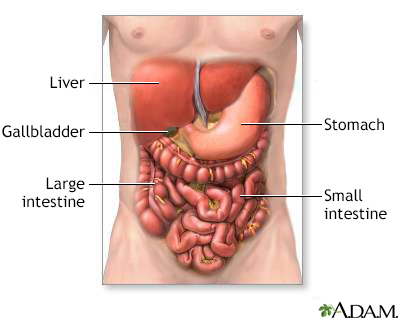 Digestive system o...
Digestive system o...
