Renovascular hypertension
Definition
Renovascular hypertension is high blood pressure due to narrowing of the arteries that carry blood to the kidneys. This condition is also called renal artery stenosis.
Alternative Names
Renal hypertension; Hypertension - renovascular; Renal artery occlusion; Stenosis - renal artery; Renal artery stenosis; High blood pressure - renovascular
Causes
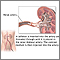
Renal artery stenosis is a narrowing or blockage of the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys.
The most common cause of renal artery stenosis is a blockage in the arteries. This problem most often occurs when a sticky, fatty substance called plaque builds up on the inner lining of the arteries, causing a condition known as atherosclerosis.
When the arteries that carry blood to your kidneys become narrow, less blood flows to the kidneys. The kidneys mistakenly respond as if your blood pressure is low. As a result, they release hormones that tell the body to hold on to more salt and water. This causes your blood pressure to rise.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Heavy alcohol use
- Cocaine use
- Increasing age
Fibromuscular dysplasia is another cause of renal artery stenosis. It is typically seen in women under age 50. It tends to run in families. The condition is caused by abnormal growth of cells in the walls of the arteries leading to the kidneys. This also leads to narrowing or blockage of these arteries.
Symptoms
People with renovascular hypertension may have a history of very high blood pressure that is hard to bring down with medicines.
Symptoms of renovascular hypertension include:
- High blood pressure at a young age
- High blood pressure that suddenly gets worse or is hard to control
- Kidneys that are not working well (this can start suddenly)
- Narrowing of other arteries in the body, such as to the legs, the brain, the eyes and elsewhere
- Sudden buildup of fluid in the air sacs of the lungs (pulmonary edema)
If you have a dangerous form of high blood pressure called malignant hypertension, symptoms�can�include:
- Bad headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Confusion
- Changes in vision
- Nosebleeds
Exams and Tests
The health care provider may hear a "whooshing" noise, called a bruit, when placing a stethoscope over your belly area where the renal arteries are.
The following blood tests may be done:
- Cholesterol levels
- Renin and aldosterone levels
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- Creatinine
- Potassium
- Creatinine clearance
Imaging tests may be done to see if the kidney arteries have narrowed. They include:
- Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition renography
- Doppler ultrasound of the renal arteries
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
- Renal artery angiography
Treatment
High blood pressure caused by narrowing of the arteries that lead to the kidneys is often hard to control.
One or more medicines are needed to help control blood pressure. There are many types available.
- Everyone responds to medicine differently. Your blood pressure should be checked often. The amount and type of medicine you take may need to be changed from time to time.
- Ask your provider what blood pressure reading is right for you.
- Take all medicines the way your provider prescribed them.
Have your cholesterol levels checked, and treated if it is needed. Your provider will help determine the right cholesterol levels for you based on your heart disease risk and other health conditions.
Lifestyle changes are important:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet.
- Exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes a day (check with your provider before starting).
- If you smoke, quit. Find a program that will help you stop.
- Limit how much alcohol you drink: 1 drink a day for women, 2 a day for men.
- Limit the amount of sodium (salt) you eat. Aim for less than 1,500 mg per day. Check with your provider about how much potassium you should be eating.
- Reduce stress. Try to avoid things that cause stress for you. You can also try meditation or yoga.
- Stay at a healthy body weight. Find a weight-loss program to help you if you need it.
Further treatment depends on what causes the narrowing of the kidney arteries. Your provider may recommend a procedure called angioplasty with stenting.
These procedures may be an option if you have:
- Severe narrowing of the renal artery
- Blood pressure that cannot be controlled with medicines
- Kidneys that are not working well and are becoming worse
However, the decision about which people should have these procedures is complex, and depends on many of the factors listed above.
Possible Complications
If your blood pressure is not well controlled, you are at risk for the following complications:
- Aortic aneurysm
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Chronic kidney disease
- Stroke
- Vision problems
- Poor blood supply to the legs
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Make an appointment with your provider if you think you have high blood pressure.
Contact your provider if you have renovascular hypertension and symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment. Also make contact if new symptoms develop.
Prevention
Preventing atherosclerosis may prevent renal artery stenosis. Taking the following steps can help:
- Lose weight if you are overweight.
- Ask your provider about your smoking and alcohol use.
- Control your blood sugar if you have diabetes.
- Make sure your provider is monitoring your blood cholesterol levels.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet.
- Get regular exercise.
References
Bakris GL, Sorrentino MJ. Systemic hypertension: mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 26.
Flack JM. Arterial hypertension. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 64.
Textor SC. Renovascular hypertension and ischemic nephropathy. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 47.
US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for hypertension in adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(16):1650-1656. PMID: 33904861 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33904861/.
|
Review Date:
5/10/2024 Reviewed By: Neil Grossman, MD, Saint Vincent Radiological Associates, Framingham, MA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. |