Weight-loss surgery
Introduction
The purpose of this tool is to help you decide whether or not to have weight-loss surgery. When making a decision like this, you must balance:
- The reasons for having the procedure
- The potential health risks, drawbacks, or limitations of the procedure
- Whether there are alternative procedures that may be more appropriate
- Cost
This tool is not a substitute for professional medical care and advice. Work with your doctor to help you make this decision. A second opinion from another doctor may be valuable. There is usually no exact “right” or “wrong” answer.
Your physician may make certain recommendations to you. However, the final decision about whether to have this test rests with you.
What is the surgery?
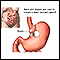
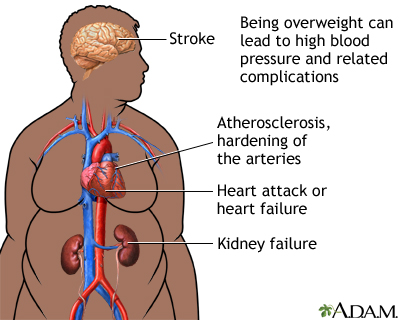
Weight-loss surgery may help some dangerously obese people. The procedure, called bariatric surgery, may lower many health risks or make certain conditions easier to treat, including heart problems, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and diabetes. This surgery may provide much greater control of weight than nonsurgical weight-loss methods. Weight-loss surgery may even significantly reduce diabetes and the need for medications to treat it. Heartburn, arthritis, and other joint and circulation problems often improve after surgery.
Bariatric surgery produces weight loss through one of two approaches:
- Restrictive procedures. Vertical banded gastroplasty and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (Lap-Band) close off parts of the stomach with bands. These procedures restrict hunger and the amount of food a patient eats. Sleeve gastrectomy is a third restrictive option. In this procedure, doctors staple off and remove part of the stomach to create a smaller stomach.
- Malabsorptive bypass procedures. The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and biliopancreatic diversion surgeries restrict the amount of food a patient eats. They also bypass parts of the intestine to reduce food absorption.
Weight-loss surgery is right for you only if you meet certain strict criteria described later in this decision tool.
Key points
- Doctors may typically recommend weight-loss surgery for obese patients who suffer from an illness such as diabetes or sleep apnea. These people usually have failed other medically supervised ways of losing weight, such as diet and exercise. Experts hotly debate which kind of weight-loss surgery is the best kind. Your doctor will help you decide which procedure is best for you.
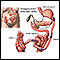
- Lap-Band is the most common weight-loss surgery worldwide, but it is less common in the U.S. Lap-Band has the least risk of any of these procedures, but it may not provide as much weight loss as other techniques. In Lap-Band, a surgeon places an adjustable silicone band around the upper part of the stomach. The band can be tightened or loosened. The procedure restricts the amount of food you can eat and makes you feel full.
- Vertical banded gastroplasty is rarely used as a first-line option. In this procedure, a surgeon creates a hole through both stomach walls and seals the edges with a staple. This narrows the stomach, similar to a funnel, and allows only small amounts of food to pass through.
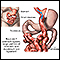
- Gastric bypass is the most common weight-loss surgery in the U.S. This procedure, however, has a greater risk for surgical complication, nutritional deficiencies, and even death. Still, gastric bypass is generally considered more effective for weight loss. In this surgery, a doctor creates a small stomach pouch. This pouch serves as a reservoir and restricts food intake.
- Biliopancreatic diversion may have the highest risk among the weight-loss surgical options, but it also may produce the greatest weight loss. Biliopancreatic diversion is usually used to treat severe cases of obesity. This procedure removes portions of the stomach and creates a pouch. The pouch attaches directly to the lower part of the small intestine.
- Sleeve gastrectomy is another restrictive procedure. This surgery is most often used as a bridge treatment for extremely obese patients before they eventually have gastric bypass surgery. In this surgery, about 60% of the stomach is removed. The remaining portion of the stomach then resembles a tube or sleeve. This procedure has less risk than gastric bypass.
- Most people who have weight-loss surgery lose about two-thirds of their excess weight within 2 years.
- Even though most patients maintain significant weight loss, the majority regain about 10% of their weight. People who have weight loss surgery must still develop a healthy lifestyle and be conscious of their calorie intake after the operation.
- Side effects and complications of weight loss surgery are common.
- Up to 25% of patients need corrective or repeat procedures.
How much time this decision tool will take
5 - 10 minutes
What this tool will provide
- A personalized list of factors for you to weigh
- Questions to ask your doctor
- Alternatives to this surgery
- Recommended reading
Reviewed By: David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine. Previously reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc. (6/6/2008)
- DeMaria, EJ. Bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(21):2176-83.
- Dixon JB, O'Brien PE, Playfair J, et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2008;299(3):316-323.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.