Pleural effusion
Definition
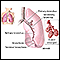
A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity.
Alternative Names
Fluid in the chest; Fluid on the lung; Pleural fluid
Causes
The body normally produces pleural fluid in small amounts to lubricate the surfaces of the pleura. This is the thin tissue that lines the chest cavity and surrounds the lungs. Pleural effusion is an abnormal, excessive collection of this fluid.
There are two types of pleural effusion:
- Transudative pleural effusion is caused by fluid leaking into the pleural space. This is from increased pressure in the blood vessels or a low blood protein count. Heart failure is the most common cause.
- Exudative effusion is caused by blocked blood vessels or lymph vessels, inflammation, infection, lung injury, or tumors.
Risk factors for pleural effusion may include:
- Smoking and drinking alcohol, as these can cause heart, lung and liver disease, which can lead to pleural effusion
- History of any contact with asbestos
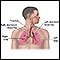
Symptoms
Symptoms can include any of the following:
- Chest pain, usually a sharp pain that is worse with cough or deep breaths
- Cough
- Fever and chills
- Hiccups
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
Sometimes there are no symptoms.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. The provider will also listen to your lungs with a stethoscope and tap (percuss) your chest and upper back.
Ultrasound of the chest, chest CT scan, or a chest x-ray may be enough for your provider to decide on treatment or the pleural effusion.
Your provider may want to perform tests on the fluid in the pleural effusion. If so, a sample of fluid is removed with a needle inserted between the ribs. Tests on the fluid will be done to look for:
- Infection
- Cancer cells
- Protein levels
- Cell counts
- Acidity of the fluid (sometimes)
Blood tests that may be done include:
- Complete blood count (CBC), to check for signs of infection or anemia
- Kidney and liver function blood tests
If needed, these other tests may be done:
- Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiogram) to look for heart failure
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
- Urine protein testing
- Lung biopsy to look for cancer
- Passing a tube through the windpipe to check the airways for problems or cancer (bronchoscopy)
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to:
- Remove the fluid
- Prevent fluid from building up again
- Determine and treat the cause of the fluid buildup
Removing the fluid (thoracentesis) may be done if there is a lot of fluid and it is causing chest pressure, shortness of breath, or a low oxygen level. Removing the fluid allows the lung to expand, making breathing easier.
The cause of the fluid buildup must also be treated:
- If it is due to heart failure, you may receive diuretics (water pills) and other medicines to treat heart failure.
- If it is due to an infection, antibiotics will be given. Sometimes additional treatment is needed.
- If it is from cancer, liver disease, or kidney disease, treatment should be directed at these conditions.
In people with cancer or infection, the effusion is often treated by using a chest tube to drain the fluid and treating its cause.
In some cases, any of the following treatments are done:
- Chemotherapy
- Placing medicine into the chest that prevents fluid from building up again after it is drained
- Leaving a small size tube in place for a longer period to let the fluid drain and the lung expand overtime
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome depends on the underlying disease.
Possible Complications
Complications of pleural effusion may include:
- Lung damage
- Infection that turns into an abscess, called an empyema
- Air in the chest cavity (pneumothorax) after drainage of the effusion
- Pleural thickening (scarring of the lining of the lung)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider or go to the emergency room if you have:
- Symptoms of pleural effusion
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing right after thoracentesis
References
Blok BK. Thoracentesis. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 9.
Broaddus VC, Light RW. Pleural effusion. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 108.
McCool FD. Diseases of the diaphragm, chest wall, pleura and mediastinum. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 86.
Reviewed By: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.