Blockage of upper airway
Definition
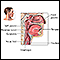
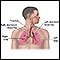
Blockage of the upper airway occurs when the upper breathing passages become narrowed or blocked, making it hard to breathe. Areas in the upper airway that can be affected are the windpipe (trachea), voice box (larynx), or throat (pharynx).
Alternative Names
Airway obstruction - acute upper
Causes
The airway can become narrowed or blocked due to many causes, including:
- Foreign bodies, such as peanuts and other breathed-in foods, pieces of a balloon, buttons, coins, and small toys are a common cause of upper airway obstruction in small children
- Allergic reactions in which swelling of the trachea or throat in response to bee sting, peanuts, and tree nuts, or medicines such as antibiotics (such as penicillin), and ACE inhibitors (a medicine to treat high blood pressure)
- Chemical burns and reactions
- Epiglottitis (infection of the structure separating the trachea from the esophagus)
- Fire or burns from breathing in smoke
- Infections of the upper airway area
- Injury to the upper airway area
- Peritonsillar abscess (collection of infected material near the tonsils)
- Poisoning from certain substances, such as strychnine
- Retropharyngeal abscess (collection of infected material in the back of the airway)
- Severe asthma attack
- Throat cancer
- Tracheomalacia (weakness of the cartilage that supports the trachea)
- Vocal cord problems
- Passing out or being unconscious, usually due to the tongue blocking the airway
People at higher risk for airway obstruction include those who have:
- Neurologic problems such as swallowing difficulty after a stroke or head injury
- Lost teeth
- Certain mental health problems
Young children and older adults are also at higher risk for airway obstruction.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary, depending on the cause. But some symptoms are common to all types of airway blockage. These include:
- Agitation or fidgeting
- Bluish color of the skin (cyanosis)
- Changes in consciousness
- Choking
- Confusion
- Difficulty breathing, gasping for air, leading to panic
- Unconsciousness (lack of responsiveness)
- Wheezing, crowing, whistling, or other unusual breathing noises indicating breathing difficulty
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a physical examination and check the airway. The provider will also ask about the possible cause of the blockage.
Tests are usually not necessary, but may include:
- Bronchoscopy (tube through the mouth into the trachea and bronchial tubes)
- Laryngoscopy (tube through the mouth into the back of the throat and voice box)
- X-rays or CT scan (computerized tomography) of the neck or chest
Treatment
The treatment depends on the cause of the blockage.
- Objects stuck in the airway may be removed with special instruments.
- A tube may be inserted into the airway (endotracheal tube) to help with breathing.
- Sometimes an opening is made through the neck into the airway (tracheostomy or cricothyrotomy).
If the obstruction is due to a foreign body, such as a piece of food that has been breathed in, doing abdominal thrusts, back blows, or chest compressions can save the person's life.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Prompt treatment is often successful. But the condition is dangerous and may be fatal, even when treated.
Possible Complications
If the obstruction is not relieved, it can cause:
- Brain damage
- Breathing failure
- Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Airway obstruction is often an emergency. Call 911 or the local emergency number for medical help. Follow instructions on how to help keep the person breathing until help arrives.
Prevention
Prevention depends on the cause of the upper airway obstruction.
The following methods may help prevent an obstruction:
- Eat slowly and chew food completely.
- Do not drink too much alcohol before or while eating.
- Keep small objects away from young children.
- Make sure dentures fit properly.
Learn to recognize the universal sign for inability to breathe due to a blocked airway: grabbing the neck with one or both hands. Also learn how to clear a foreign body from the airway using a method such as abdominal thrusts.
References
Robinson AE, Driver BE, Reardon RF. Basic airway management and decision-making. In: Birnbaumer DM, ed. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 3.
Goodloe JM, Soulek J. Foreign bodies. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 51.
Rose E. Pediatric upper airway obstruction and infections. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 162.
Reviewed By: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.