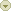
The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates bile produced in the liver. Bile aids in the digestion of fats, and is released from the gallbladder into the upper small intestine (duodenum) in response to food, especially fats. Types of gallbladder disease include:
You can have gallstones without any symptoms. However, if the stones are large, they can block the duct that leads from the gallbladder. This can cause pain and require treatment. At first they may block the duct and move away, causing only occasional pain. Continuous blockage of the duct, however, can be life threatening and requires surgical removal of the gallbladder.
Signs and Symptoms
What Causes It?A gallbladder attack usually happens because a stone is blocking a passageway in the gallbladder. Gallstones develop in the gallbladder when substances in bile form hard particles. They can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. Women are at higher risk of developing gallstones than men, and the risk increases the more children a woman has had. Pregnancy is also a risk for gallstone formation. The increased risk associated with having children can be offset by breastfeeding. Women who use hormone replacement therapy are also at higher risk of developing gallstones. Being overweight and rapid weight loss followed by weight gain are other risk factors for gallstones. Having coronary artery disease is also associated with gallbladder disease.
What to Expect at Your Doctor's OfficeIf you are having a gallbladder attack, you will feel tenderness when the upper right side of your abdomen is touched. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin) occurs when the bile duct (a tube between the liver and gallbladder) is also blocked. If your doctor thinks you have a gallstone, you will probably need an ultrasound. During an ultrasound, sound waves take pictures of your gallbladder. This test is fast and painless.
Treatment OptionsDoctors typically remove gallbladders that cause pain. There are no known problems caused by living without a gallbladder. Today, most gallbladder surgeries are performed with a laparoscope. This instrument shows the surgeon pictures of your gallbladder as it is being removed. The minimally invasive procedure allows for a smaller incision and a shorter hospital stay than traditional surgery. Some drugs can dissolve stones, eliminating the need for surgery. They include:
However, it can take 2 years for a stone to dissolve, and gallstones often return.
Complementary and Alternative TherapiesGallstones should always be treated by a doctor. If you would like to add complementary remedies to your treatment, see your doctor for tests before you start any therapies. This will help determine the remedies that are right for the size of your stone and your condition. DO NOT attempt complementary and alternative therapies (CAM) on your own. Work with an experienced provider. Keep all of your physicians informed regarding CAM, as some therapies may interfere with conventional medical treatments. Work with a provider who is knowledgeable in complementary medicine to find the right mix of treatments for you. If you are pregnant, or thinking about becoming pregnant, do not use any CAM therapies unless directed to do so by your physician. Nutrition and SupplementsThese nutritional tips may help reduce symptoms:
You may address nutritional deficiencies with the following supplements:
HerbsHerbs are a way to strengthen and tone the body's systems. As with any therapy, you should work with your doctor before starting any treatment. You may use herbs as dried extracts (capsules, powders, or teas), glycerites (glycerine extracts), or tinctures (alcohol extracts). People with a history of alcoholism should not take tinctures. Unless otherwise indicated, make teas with 1 tsp. herb per cup of hot water. Steep covered 5 to 10 minutes for leaf or flowers, and 10 to 20 minutes for roots. Drink 2 to 4 cups per day. You may use tinctures singly or in combination as noted. If you are pregnant or nursing, speak to your doctor before using any herbal products. A gallbladder attack can be a medical emergency. DO NOT use herbs to treat gallbladder disease on your own. Work with a trained herbal practitioner under the supervision of your doctors. The following herbs are sometimes used to treat gallbladder disease:
HomeopathyFew clinical studies have examined the effectiveness of specific homeopathic remedies. However, a professional homeopath may recommend one or more of the following treatments for gallbladder disease based on their knowledge and clinical experience. Before prescribing a remedy, homeopaths take into account a person's constitutional type, includes your physical, emotional, and intellectual makeup. An experienced homeopath assesses all of these factors when determining the most appropriate remedy for a particular individual. Some of the most common remedies are listed below. A common dose is 3 to 5 pellets of a 12X - 30C remedy every 1 to 4 hours until your symptoms improve.
Physical MedicineCastor oil pack. Apply oil to a clean, soft cloth and place on abdomen. Cover with plastic wrap, place a heat source (hot water bottle or heating pad) over the pack, and let sit for 30 to 60 minutes. For best results, use for 3 consecutive days. Apply to abdomen, especially the gallbladder area, to help reduce swelling. AcupunctureAcupuncture may be especially helpful in pain relief, reducing spasm, easing bile flow, and restoring proper liver and gallbladder function.
Following UpEarly surgery usually ends symptoms and recurrence. Stones may appear again in the bile duct, however.
Special ConsiderationsIf you have diabetes or are pregnant, you have a higher risk of complications from gallbladder attacks. If you are pregnant, use choleretic (bile-stimulating) herbs with caution. Milk thistle and dandelion root are safe in pregnancy. Talk with your health care provider before you take any medication or supplement.
Supporting ResearchAllan PL, Baxter GM, Weston MJ, eds. Clinical Ultrasound. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2011. Cabrera C, Artacho R, Gimenez R. Beneficial effects of green tea -- a review. J Am Coll Nutr. 2006;25(2):79-99. Etminan M. Oral contraceptives and the risk of gallbladder disease: a comparative safety study. CMAJ. 2011:183(8):899-904. Gaby AR. Nutritional approaches to prevention and treatment of gallstones. Altern Med Rev. 2009:14(3):258-67. Jeong SU, Lee SK. Obesity and gallbladder diseases. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012;59(1):27-34. Jiang ZY, Sheng X, Xu CY, et al. Gallbladder gallstone disease is associated with newly diagnosed coronary artery atherosclerotic disease: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75400. Ko, CW. Prefac: Gallbladder disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2010;39(2):xiii. Liu B, Beral V, Balkwill A. Childbearing, breastfeeding, other reproductive factors and the subsequent risk of hospitalization for gallbladder disease. Int J Epidemiol. 2009;38(1):312-8. Liu B, Beral V, Balkwill A, et al. Gallbladder disease and use of transdermal versus oral hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women: a prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2008;337:a386. Marx J, Hockberger R, Walls R, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine. 8th ed. Philadelphia PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014. Rai A, Tewari M, Mohapatra SC, et al. Correlation of nutritional parameters of gallbladder cancer patients. J Surg Oncol. 2006;93(8):705-8. Shaffer EA. Gallstone disease: Epidemiology of gallbladder stone disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20(6):981-96. Tsai CJ, Leitzmann MF, Willett WC, et al. Long-Term Effect of Magnesium Consumption on the Risk of Symptomatic Gallstone Disease Among Men. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; [Epub ahead of print]. Venneman NG, van Erpecum KJ. Gallstone disease: Primary and secondary prevention. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20(6):1063-73. Völzke H, Baumeister SE, Alte D, et al. Independent risk factors for gallstone formation in a region with high cholelithiasis prevalence. Digestion. 2005;71(2):97-105. Walcher T, Haenle MM, Mason RA, et al. The effect of alcohol, tobacco and caffeine consumption and vegetarian diet on gallstone prevalence. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22(11):1345-51. Wang F. Oral contraceptives and risk of gallbladder disease. CMAJ. 2011:183(13):1517.
Review Date:
4/1/2016 Reviewed By: Steven D. Ehrlich, NMD, Solutions Acupuncture, a private practice specializing in complementary and alternative medicine, Phoenix, AZ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. No warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability, timeliness, or correctness of any translations made by a third-party service of the information provided herein into any other language. © 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited. All content on this site including text, images, graphics, audio, video, data, metadata, and compilations is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws. You may view the content for personal, noncommercial use. Any other use requires prior written consent from Ebix. You may not copy, reproduce, distribute, transmit, display, publish, reverse-engineer, adapt, modify, store beyond ordinary browser caching, index, mine, scrape, or create derivative works from this content. You may not use automated tools to access or extract content, including to create embeddings, vectors, datasets, or indexes for retrieval systems. Use of any content for training, fine-tuning, calibrating, testing, evaluating, or improving AI systems of any kind is prohibited without express written consent. This includes large language models, machine learning models, neural networks, generative systems, retrieval-augmented systems, and any software that ingests content to produce outputs. Any unauthorized use of the content including AI-related use is a violation of our rights and may result in legal action, damages, and statutory penalties to the fullest extent permitted by law. Ebix reserves the right to enforce its rights through legal, technological, and contractual measures. |